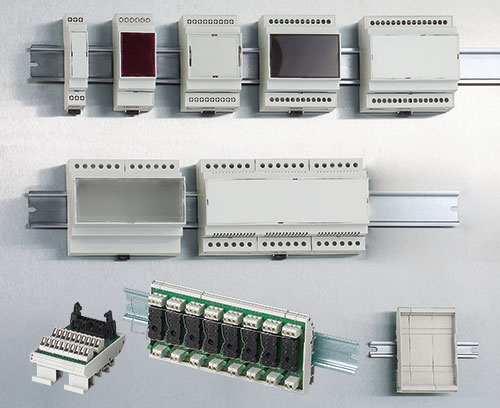
When it comes to powering homes, offices, or factories, the type of panelboard you choose makes a big difference. Whether it’s single-phase or three-phase, each has its own role in how electricity is distributed and managed. Choosing the right one isn’t just about wiring — it affects efficiency, cost, and safety.
If you’re curious about how these systems work and which one fits your setup best, this guide will break it all down. From how power flows to what each system is best suited for, we’ve got you covered in simple terms. Let’s explore what really sets them apart.
What is a Panelboard?
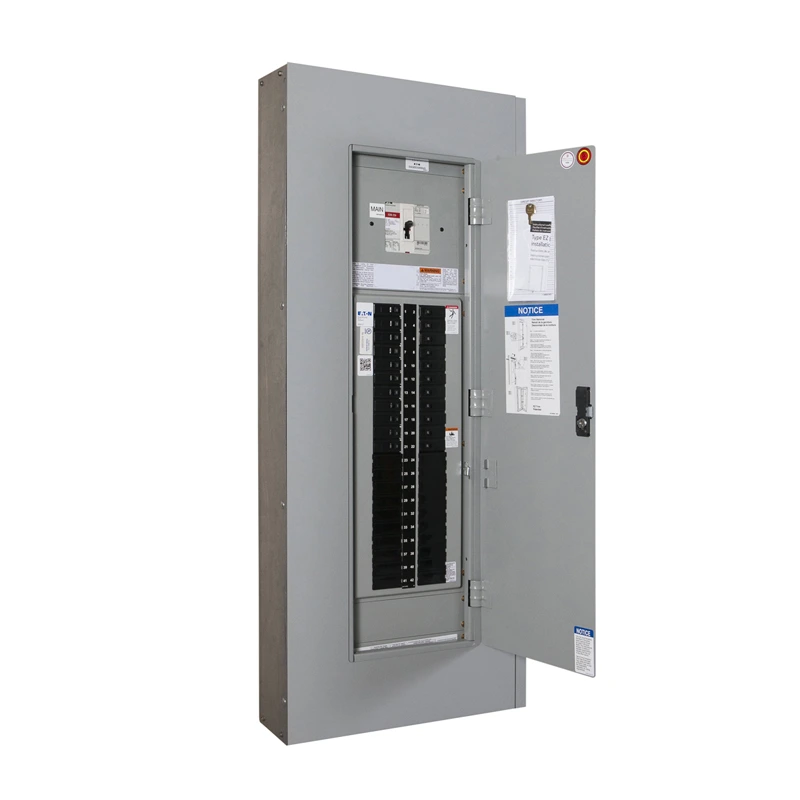

A panelboard is an important part of any electrical system. It acts like a central hub that takes in electric power from a main source and then distributes it to different circuits. These circuits power the lights, appliances, and equipment in homes, offices, or factories.
Inside a panelboard, you’ll find circuit breakers or fuses, which are safety devices that protect against overloads and short circuits. If there’s too much current flowing, the breaker will trip to stop damage or fire.
Panelboards are installed in a metal enclosure, keeping all components organized and safe from accidental contact. They’re designed to make maintenance easy and ensure safe power distribution across the entire building.
Understanding Phases in Electricity
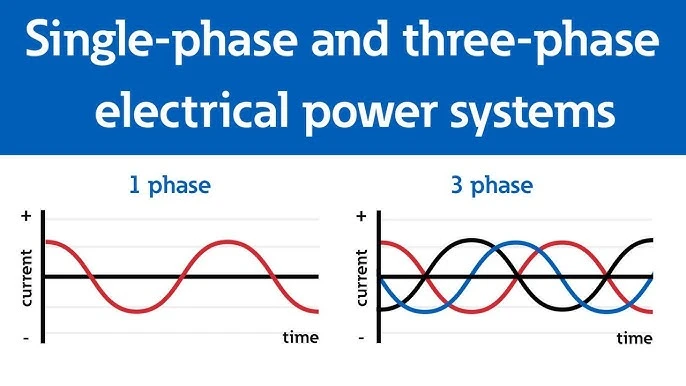
In electrical terms, a phase refers to the flow of current in a cyclical wave pattern. Most of the power we use is alternating current (AC), which means the direction of the current changes repeatedly over time. These changes create a waveform — an up-and-down pattern that shows how voltage rises and falls.
Single-Phase
In a single-phase system, there is one wave of current flowing through the circuit. This wave rises and falls in a smooth cycle, but it reaches zero between cycles. That means the power delivery isn’t constant — there are brief moments where no power flows.
Three-Phase
In contrast, a three-phase system uses three separate waves, each starting at a different point in time (120 degrees apart). This setup ensures that at least one wave is always at its peak, which provides a more steady and reliable flow of power.
What is a Single-Phase Panelboard?
A single-phase panelboard is designed to manage power in systems that use a single alternating current (AC) waveform. It typically has two or three wires – one or two hot wires and one neutral wire. This setup is simple and ideal for low power needs.
The main components include circuit breakers, bus bars, and a neutral bar. These work together to control and protect electrical circuits in homes or small buildings.
The voltage levels usually vary by region. In countries like the U.S., it’s commonly 120V/240V, while in places like India, it’s around 230V.
What is a Three-Phase Panelboard?
A three-phase panelboard is built for systems that carry three alternating current (AC) waveforms, each spaced 120 degrees apart. It typically has three or four wires – three hot wires and sometimes a neutral. This setup allows for constant and balanced power flow, making it ideal for heavy electrical loads.
Structurally, it’s more complex than a single-phase panelboard. It includes larger bus bars, multiple breakers, and often a grounding system to handle higher current levels safely. Functionally, it delivers continuous power, reducing stress on equipment and improving efficiency.
In many regions like India, the standard voltage for a three-phase system is 415V. This higher voltage supports larger machines and power-hungry operations.
Key Differences: Single Phase vs Three Phase Panelboards
| Factor | Single Phase | Three Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Power Delivery | Delivers power in one wave with brief pauses | Constant flow using three waves, no power drop |
| Efficiency | Less efficient for heavy loads | Highly efficient, especially for industrial needs |
| Load Capacity | Best for small loads like home appliances | Handles large machines and continuous operations |
| Cost | Lower initial cost and maintenance | Higher cost but better long-term value for big setups |
| Design Complexity | Simple to install and maintain | Complex setup, requires trained professionals |
| Safety | Safe for home and light commercial use | Needs advanced safety measures due to high voltage |
| Best For | Homes, small offices, shops | Industries, data centers, large commercial buildings |

Let’s break down the main differences between single-phase and three-phase panelboards.
Power Delivery
Single-phase systems deliver power in one wave, which rises and falls. There are small gaps when the wave reaches zero, which means the power isn’t always steady.
In contrast, three-phase systems use three waves spaced apart, so at least one wave is always active. This gives a continuous power supply, which is smoother and more reliable.
Efficiency
Single-phase is good for basic tasks, but it becomes less efficient when you connect too many devices.
Three-phase systems are designed to carry more power with less energy loss. They handle bigger loads better and waste less electricity during transmission.
Load Capacity
If you’re just powering lights, fans, and a fridge, single-phase is enough.
But for industrial machines, HVAC systems, or elevators, you need more power. That’s where three-phase panelboards shine—they can handle large and continuous loads without strain.
Cost
Single-phase systems are cheaper to install and maintain. They have fewer components and a simpler setup.
Three-phase systems cost more upfront but are more economical in the long run for large buildings and factories due to their efficiency.
Design Complexity
A single-phase panelboard is easy to install and troubleshoot. It’s beginner-friendly.
Three-phase boards are more complex, requiring professional installation and extra safety precautions.
Safety
Both systems are safe when installed properly.
But because three-phase systems deal with higher voltages and current, they need stronger safety measures and regular checks to avoid risks.
Best Use Cases
Single-phase panelboards are widely used in residential homes and shops, where the demand for electricity is moderate. They are perfect for running lights, fans, and home appliances.
Three-phase panelboards are commonly used in data centers, large commercial buildings, and industrial plants. They’re essential where machinery operates continuously.
FAQs on Single-Phase vs Three-Phase Panelboards
Yes, but it’s usually not needed. Homes don’t require high power, so a single-phase panelboard is enough. A three-phase setup may only make sense if you have large appliances or special equipment.
Yes, it generally costs more due to extra wiring, equipment, and professional setup. However, for large buildings or industrial use, it can save money in the long run through better power efficiency.
Yes, but it may require changing the wiring, panelboard, and getting utility company approval. It’s best to plan your power needs early to avoid extra costs and work later.
Both are safe when installed correctly, but three-phase systems need stronger safety checks due to higher voltage. Regular maintenance and professional handling are important for safety.
Industries use machines that need steady and strong power. Three-phase systems deliver that with less energy loss, making them more reliable and cost-effective for high-power environments.
Conclusion
Choosing between a single-phase and three-phase panelboard depends on your power needs, budget, and usage environment. If you’re running a home or a small office, a single-phase system is affordable, easy to install, and handles everyday appliances just fine. But for factories, large buildings, or places with heavy equipment, a three-phase panelboard offers better performance, steady power, and long-term efficiency.
Both systems are safe and reliable when installed correctly, but it’s important to choose based on your actual requirements. Upgrading from one to the other is possible but can be costly and complex, so it’s best to plan ahead.
Looking for safe and durable electrical enclosures? At Eabel, we specialize in high-quality solutions tailored to your needs. From customized solutions to server rack cabinets, our products are designed for reliability and efficiency. Partner with us Today and experience excellence in every enclosure.
Related Read
Understanding Panelboards, Switchboards, and Switchgear in Modern Electrical Systems
What is the Difference Between Electrical Control Panels and Electrical Enclosures?
How to Ground an Electrical Panel: A Complete Guide
What is an Electrical Enclosure? Types, Materials & Uses
What is the Most Efficient Cooling Solution for Small Data Centres?